Table des matières
Capteurs - pH
[Mise à jour le 7/7/2022]
Généralités
![]() Le sigle “pH” désigne le Potentiel d'Hydrogène dans l'eau dont dépend l'acidité de l'eau : une eau acide possède un pH bas, une eau trop basique possède un pH élevé ; et on considère une eau neutre celle dont le pH est à 7,0.
Le sigle “pH” désigne le Potentiel d'Hydrogène dans l'eau dont dépend l'acidité de l'eau : une eau acide possède un pH bas, une eau trop basique possède un pH élevé ; et on considère une eau neutre celle dont le pH est à 7,0.
Plus souvent, le pH mesure l’acidité ou la basicité d’une solution. Ainsi, dans un milieu aqueux à 25 °C :
- une solution de pH = 7 est dite neutre ;
- une solution de pH < 7 est dite acide ; plus son pH diminue, plus elle est acide ;
- une solution de pH > 7 est dite basique ; plus son pH augmente, plus elle est basique.Wikipédia
Sonde pH + interface pro SEN0169

- Source : wiki
Sonde pH professionnelle DFRobot avec interface compatible Arduino permettant de mesurer un pH entre 0 et 14 à une température comprise entre 0 et +60 °C. Ce module se raccorde sur une entrée analogique d'une carte compatible Arduino ou directement sur le shield d'expansion E/S via le cordon inclus.
L'utilisation de cette sonde doit se faire dans un liquide au repos et électriquement neutre.
- Distributeur : Gotronic
- Caractéristiques
- Alimentation: 5 Vcc
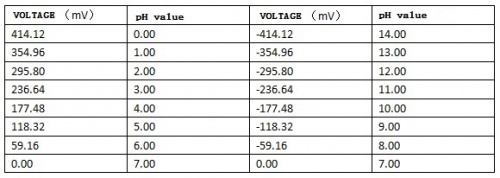
- Plage de mesure de pH: 0 à 14
- Température de fonctionnement: 0 à 60 °C
- Précision: ± 0,1 pH (25 °C)
- Temps de réponse: ≤ 1min
- Dimensions:
- sonde: Ø33 x 180 mm
- interface: 43 x 32 x 15 mm
- Tube en plastique résistant aux chocs.
- La sonde est livrée avec 5 m de câble et un connecteur BNC.
![]()
- Documentation
- Modèle de la sonde de pH
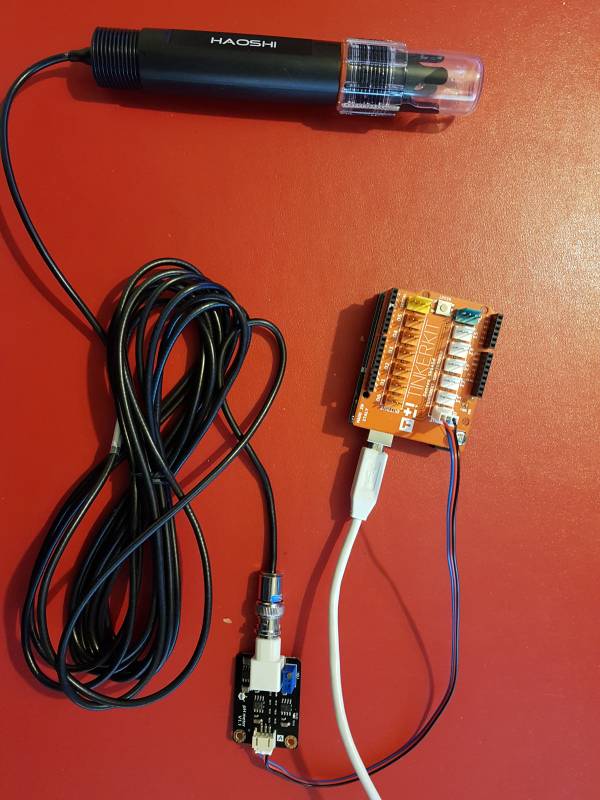
- Connexion à un shield Tinkerkit v2 monté sur une Arduino Uno

- Un premier exemple pour tester le capteur
![]()
- ph.cpp
/* # This sample code is used to test the pH meter V1.0. # Editor : YouYou # Ver : 1.0 # Product: analog pH meter # SKU : SEN0161 */ #define SensorPin A0 //pH meter Analog output to Arduino Analog Input 0 #define Offset 0.00 //deviation compensate #define LED 13 #define samplingInterval 20 #define printInterval 800 #define ArrayLenth 40 //times of collection int pHArray[ArrayLenth]; //Store the average value of the sensor feedback int pHArrayIndex=0; void setup(void) { pinMode(LED,OUTPUT); Serial.begin(9600); Serial.println("pH meter experiment!"); //Test the serial monitor } void loop(void) { static unsigned long samplingTime = millis(); static unsigned long printTime = millis(); static float pHValue,voltage; if(millis()-samplingTime > samplingInterval) { pHArray[pHArrayIndex++]=analogRead(SensorPin); if(pHArrayIndex==ArrayLenth)pHArrayIndex=0; voltage = avergearray(pHArray, ArrayLenth)*5.0/1024; pHValue = 3.5*voltage+Offset; samplingTime=millis(); } if(millis() - printTime > printInterval) //Every 800 milliseconds, print a numerical, convert the state of the LED indicator { Serial.print("Voltage:"); Serial.print(voltage,2); Serial.print(" pH value: "); Serial.println(pHValue,2); digitalWrite(LED,digitalRead(LED)^1); printTime=millis(); } } double avergearray(int* arr, int number){ int i; int max,min; double avg; long amount=0; if(number<=0){ Serial.println("Error number for the array to avraging!/n"); return 0; } if(number<5){ //less than 5, calculated directly statistics for(i=0;i<number;i++){ amount+=arr[i]; } avg = amount/number; return avg; }else{ if(arr[0]<arr[1]){ min = arr[0];max=arr[1]; } else{ min=arr[1];max=arr[0]; } for(i=2;i<number;i++){ if(arr[i]<min){ amount+=min; //arr<min min=arr[i]; }else { if(arr[i]>max){ amount+=max; //arr>max max=arr[i]; }else{ amount+=arr[i]; //min<=arr<=max } }//if }//for avg = (double)amount/(number-2); }//if return avg; }
![]()
Le projet pour l'IDE VSCode de l'exemple ci-dessus est téléchargeable ici